Today, we’re announcing a new release of Moondream 1.9B. It has improvements across a bunch of areas and includes a new capability, Gaze Detection. This release marks the first time we’ve focused on industry benchmarks, and we’re excited to share some results. Despite these upgrades, the model is still just 1.9B, so it's fast and can run everywhere. Try it out in our playground or download it now.
1. Structured Output
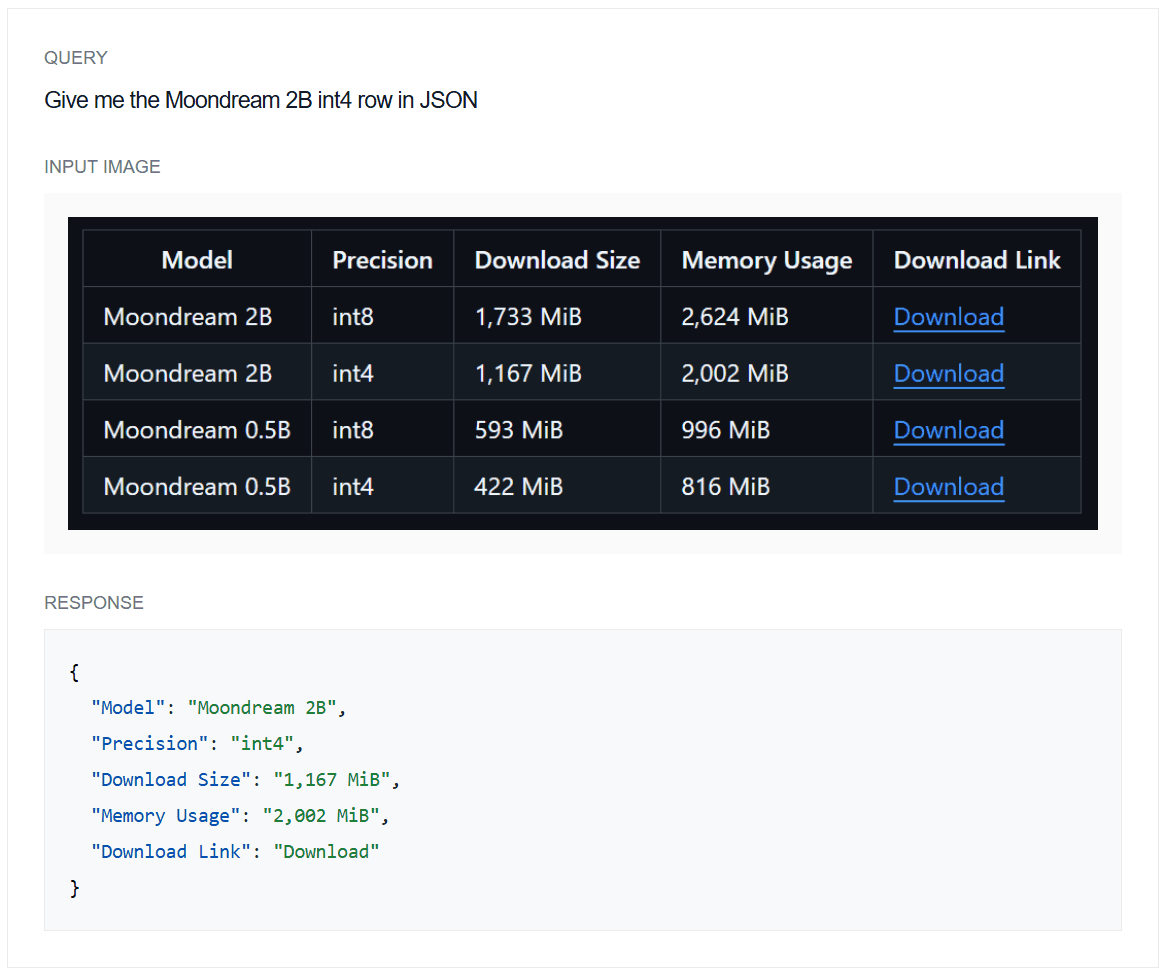
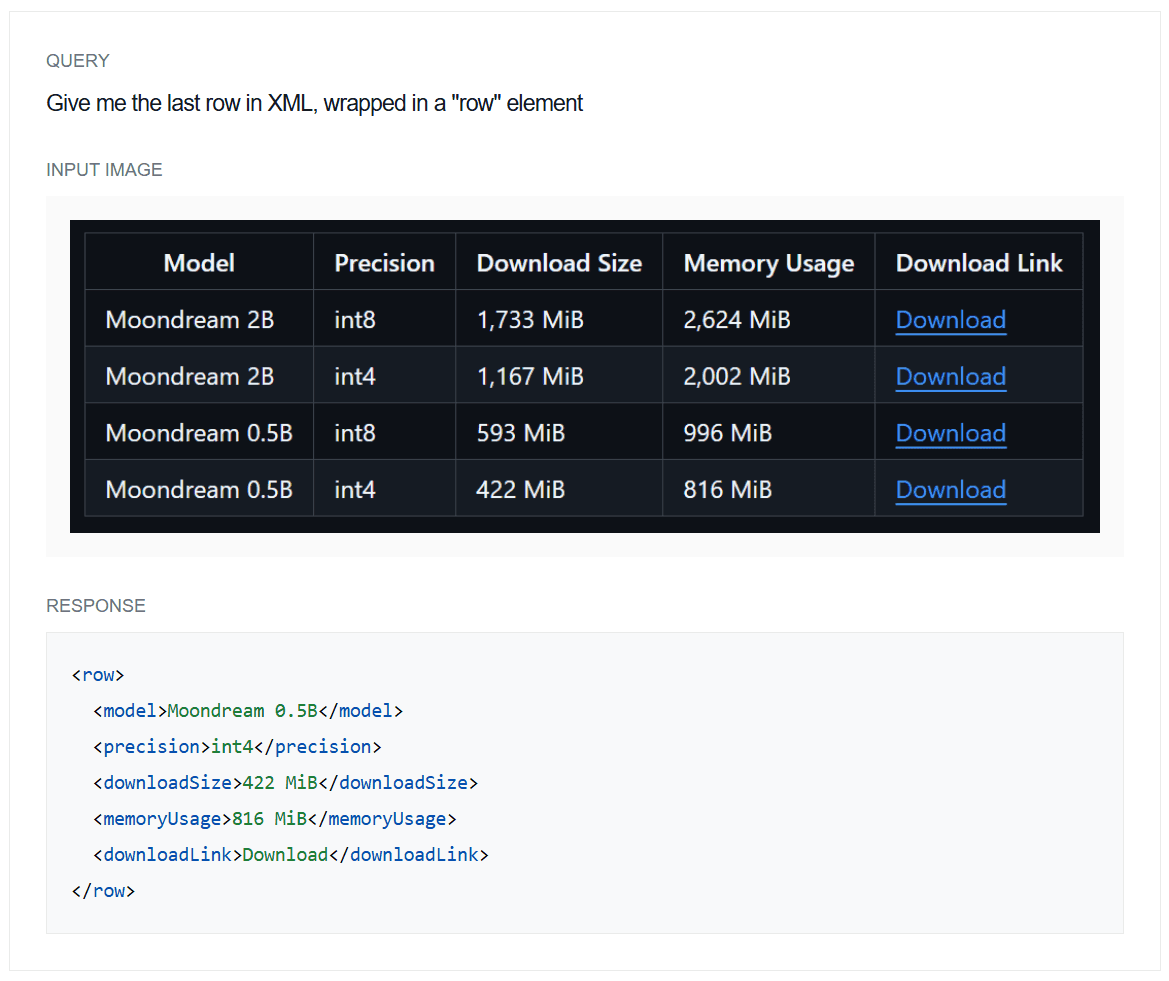
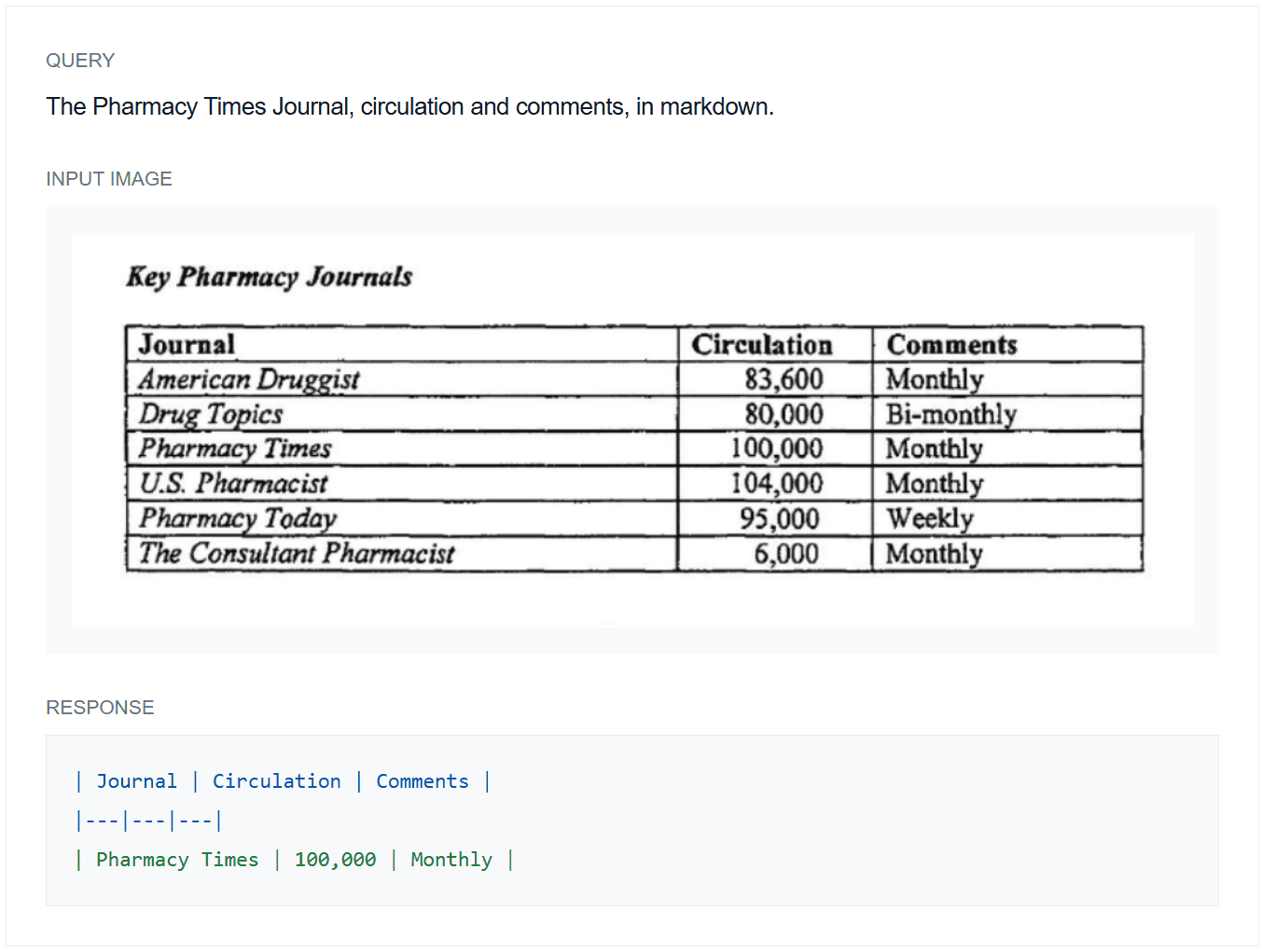
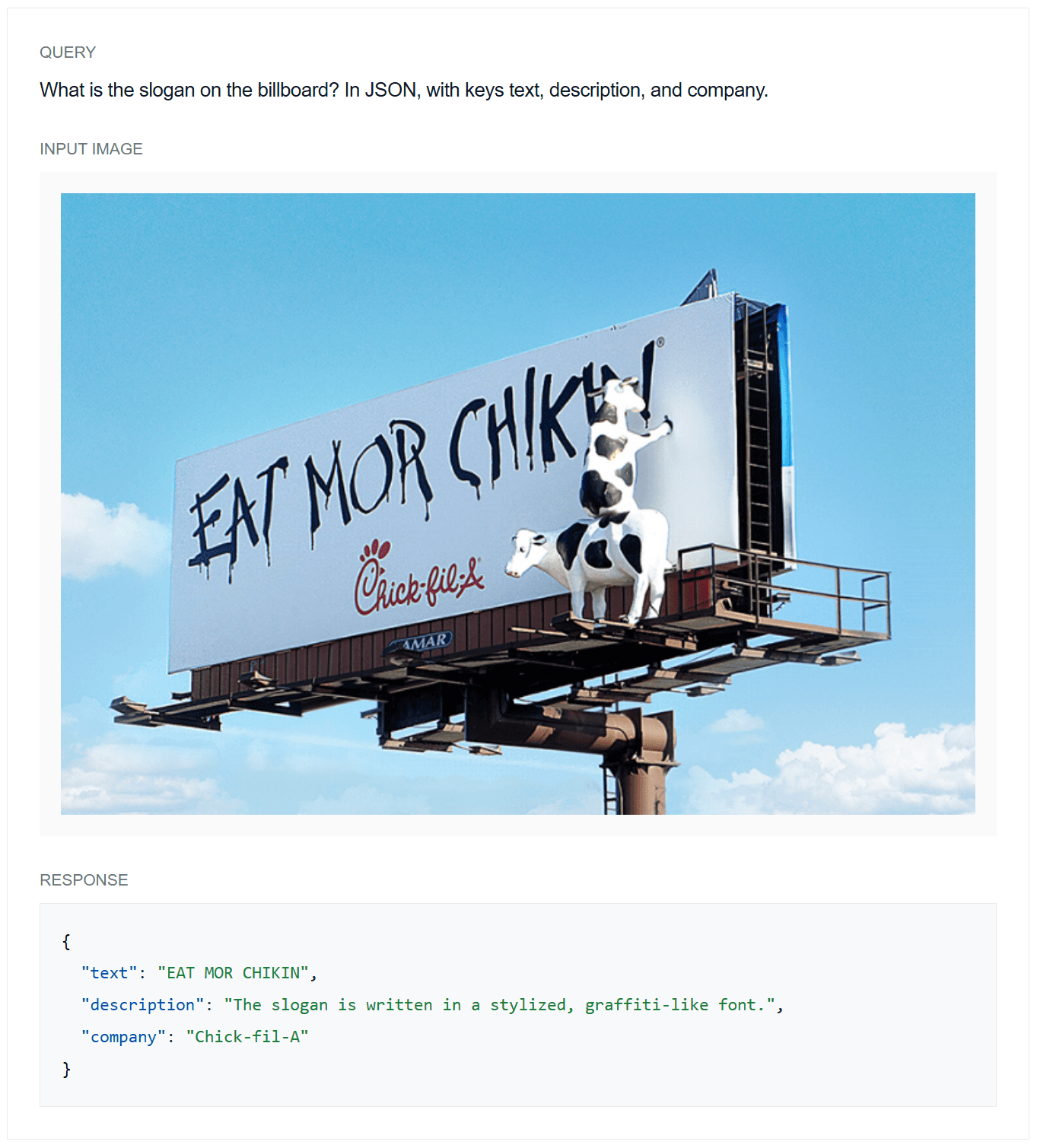
Building with Moondream is easier than ever with our new support for structured output formats such as JSON, XML, Markdown, and CSV. Here’s some examples:
Example 1: JSON structured output
Example 2: XML structured output
Example 3: Markdown structured output
2. New Capability: Gaze Detection
Traditional Vision AI consists of specialized models built for different tasks like “object detection” (outline a specified object's region in an image) or “captioning” (create a caption for an image). Moondream supports several of these common Vision AI tasks as “capabilities,” all within a single model. Moondream already supports object detection and captioning, as well as “visual querying” (ask any question to a photo) and “pointing” (get the x,y coordinates of elements within a photo).
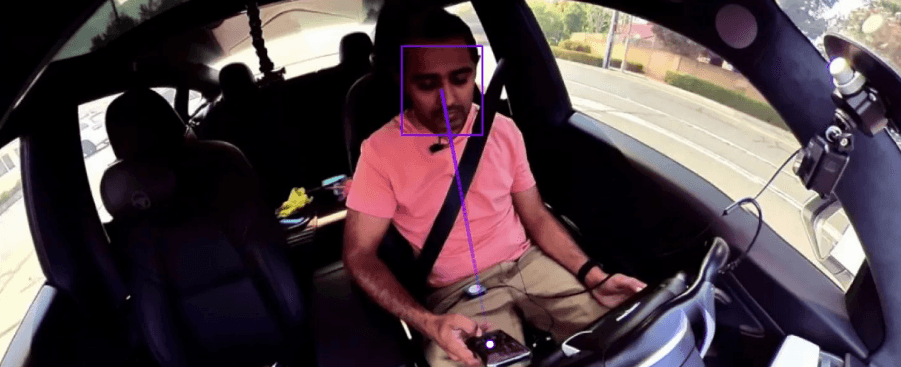
Today, we are excited to launch a new capability: Gaze Detection.
This capability tracks human attention. Note that this capability is experimental. We’re releasing it to get feedback from developers so we can improve it over time.
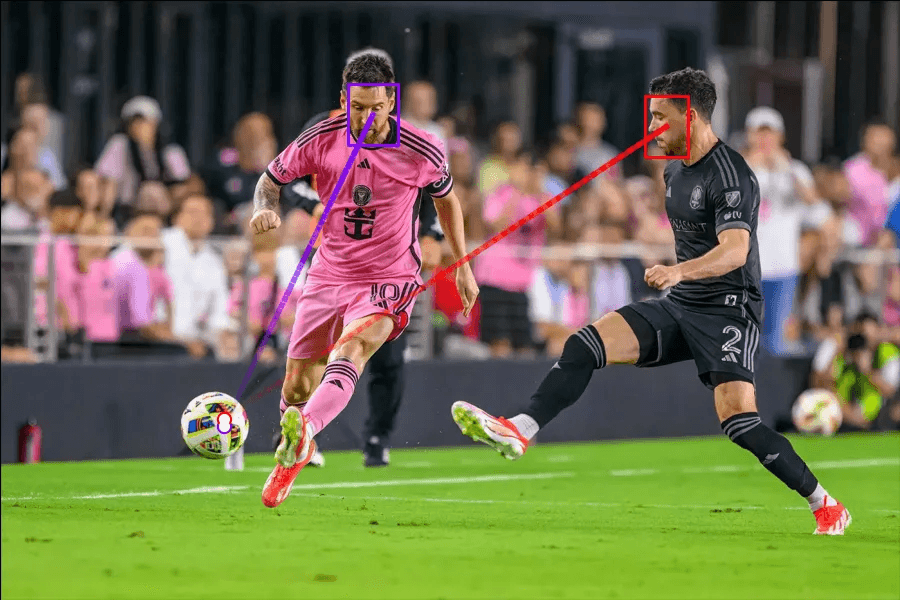
Example 1: Driver Gaze Detection
Example 2: Sport Gaze Detection
3. Benchmarks
We’ve always been a bit iffy about benchmarks. Some focus on problems we don’t think are relevant to Moondream (e.g., solving math equations). Others include weird questions and wrong answers (at least to us — see the Weird Benchmarks appendix below). And focusing too much on benchmarks can lead to weird behaviors, with allegations that some models "cheat" by training on the actual benchmarks themselves.
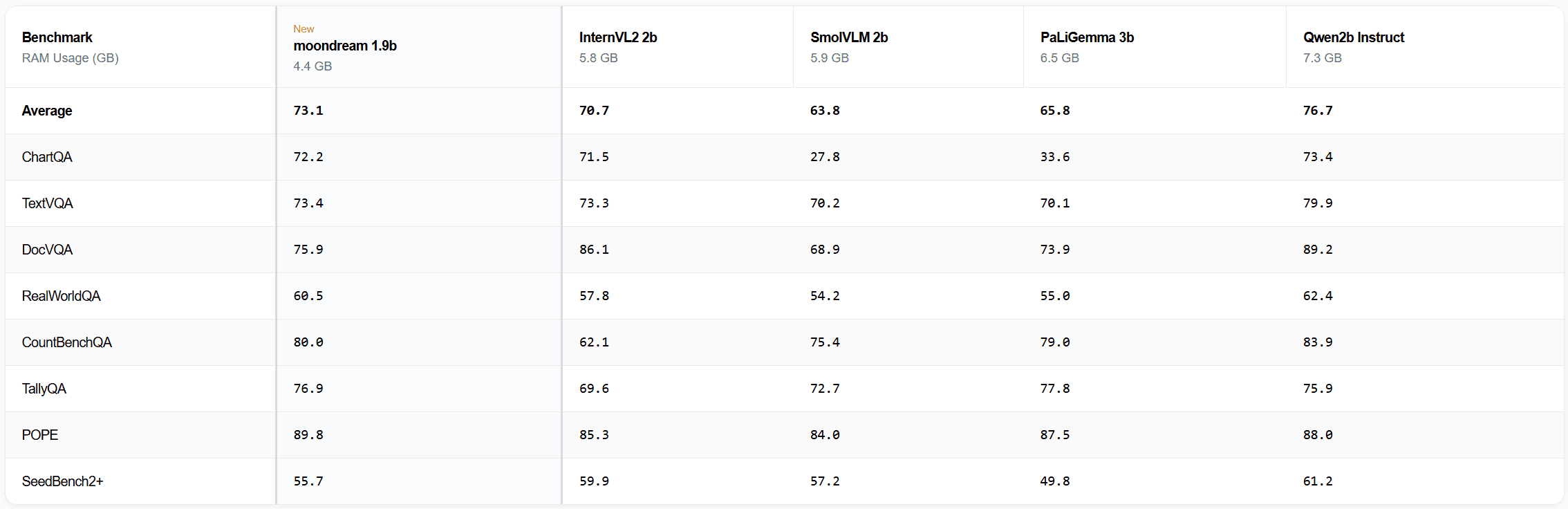
Despite this, we decided to improve our scores because we don’t want anyone sleeping on Moondream because of low results. We benchmarked ourselves along with the top small vision language models.
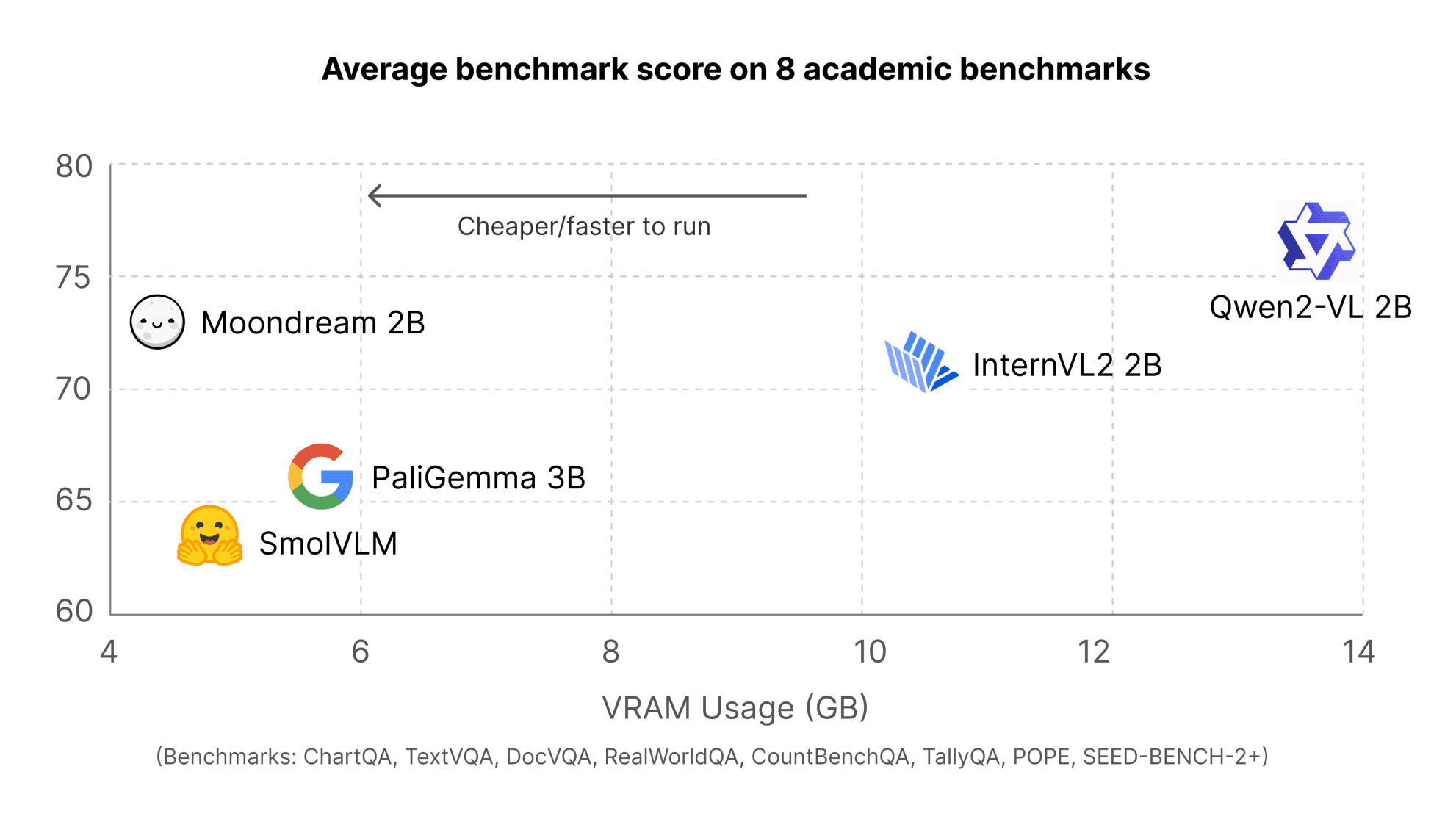
You can find our individual benchmark results below:
4. Better OCR
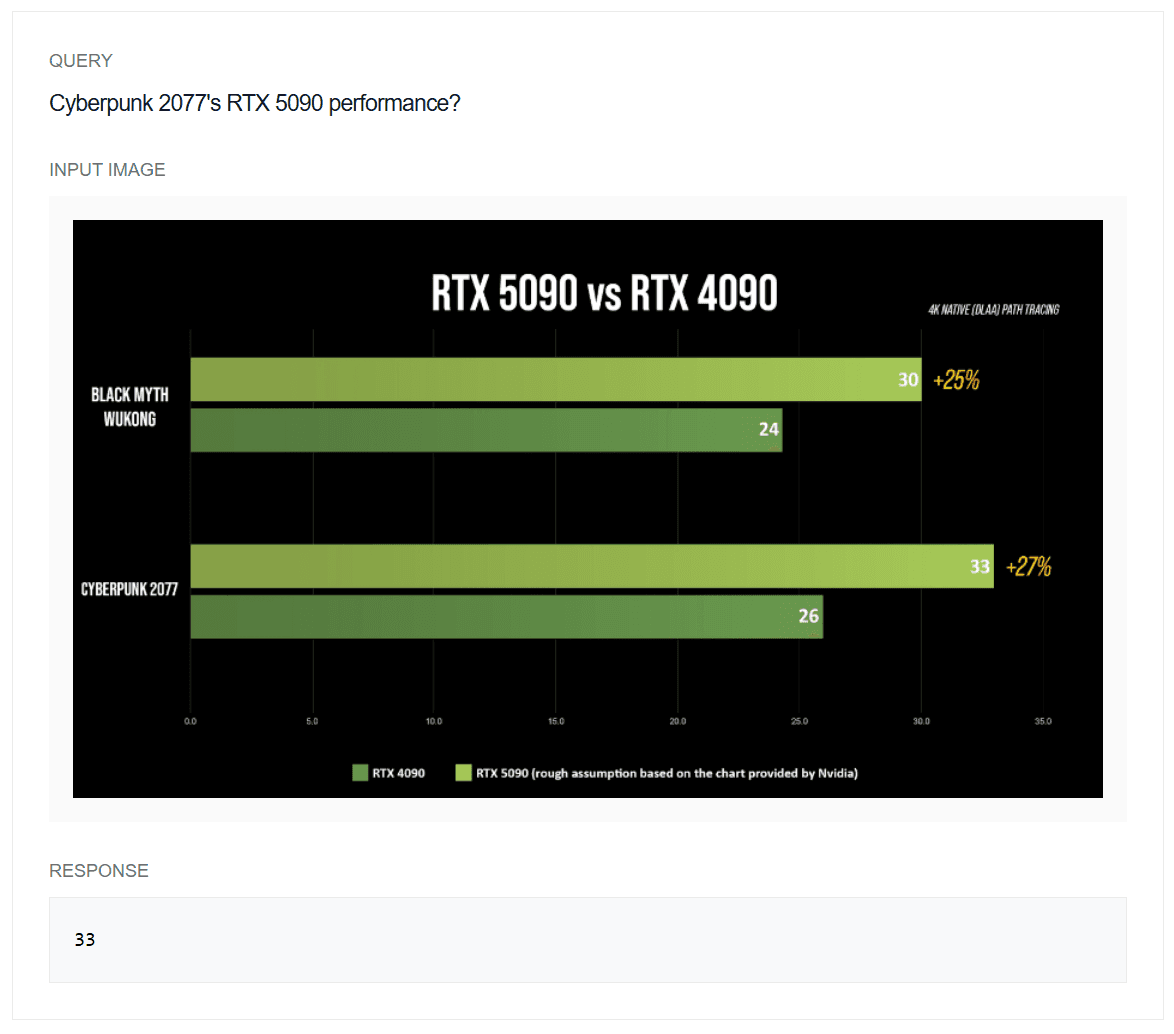
We made changes to Moondream’s vision layer that have helped improve text reading/OCR significantly. We’ve also trained it on a lot more document querying and understanding. Here’s some examples:
Example 1: OCR Example
Example 2: Chart OCR Example
Looking Ahead
As pumped as we are about this release, the best part, for us, is seeing what you build with it. VLMs are making it faster, cheaper, and easier than ever to build next generation vision-enabled apps. Getting setup takes minutes, or you can try out Moondream in our playground. We offer Cloud inference with a generous free tier, or you can download it and run it yourself. Check out our docs for a getting started guide and lots of sample code.
Happy Moondreaming!
Appendix 1: Weird Benchmark Questions
Here’s a few examples of weird benchmark questions...
Example 1: Confusing Benchmark Question
In GQA, the following image has a question that asks “Is the traffic signal on the right side or the left?” If you look closely, you can see there are traffic lights on both sides of the street. However, GQA expects the answer to be “Left.”
Example 2: Nonsensical Benchmark Question In the following image, GQA asks “What animal sits in the bench that is on the right side?" It expects the answer to be “bird” 🤯.